Asymptomatic carotid stenosis stenting
A 60-year-old male with a history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, COPD, coronary artery disease, and former alcohol abuse was referred for evaluation of a significant left carotid stenosis.
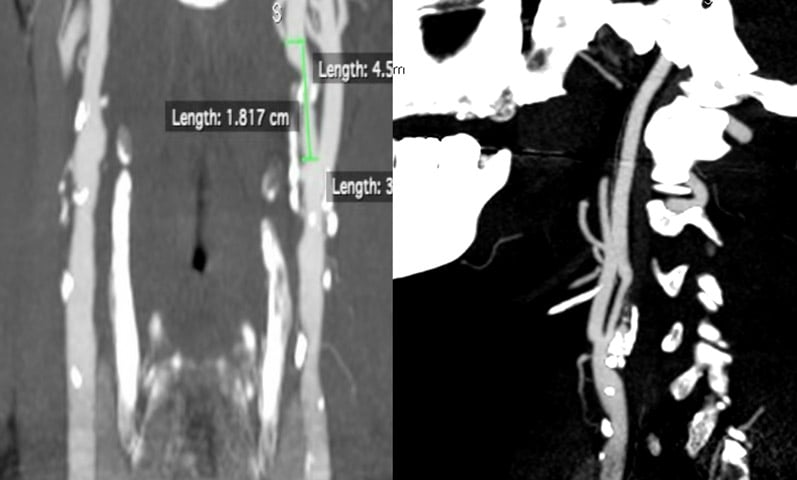
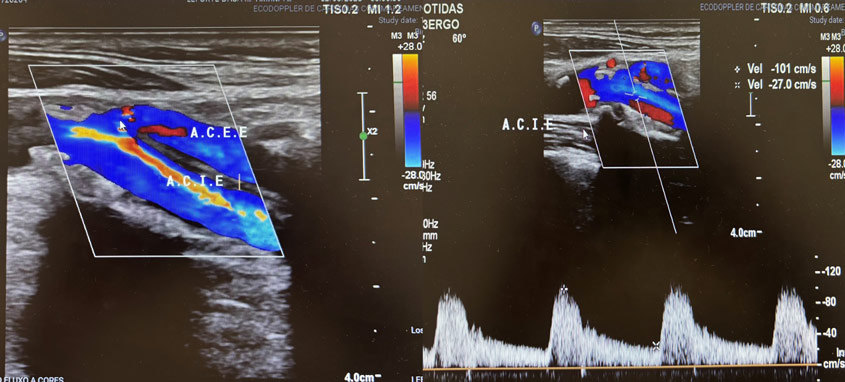
Recent imaging confirmed a > 70% stenosis with calcified ulceration in the left internal carotid artery, in the context of diffuse parietal disease and a Type I aortic arch. The patient was on dual antiplatelet therapy and had undergone cardiac arrhythmia ablation three months earlier.
Find out which revascularisation strategy was chosen and how the intervention was safely carried out in this high-risk profile.
History
- A 60 year-old male patient referred by the cardiologist
- No previous TIA / stroke
- Hypertension/ dyslipidemia/ heavy smoker - COPD/ CAD, former chronic alcoholic
- PO cardiac arrhythmia ablation Dec/24’
- Treatment: 💊 DAPT (Aspirin + Ticagrelor) + Statin + 4 classes of antihypertensives (angiotensin II receptor blocker twice a day, calcium channel blocker twice a day, beta blocker once a day, thiazide diuretic once a day).
Cardiac status: 65 % FE
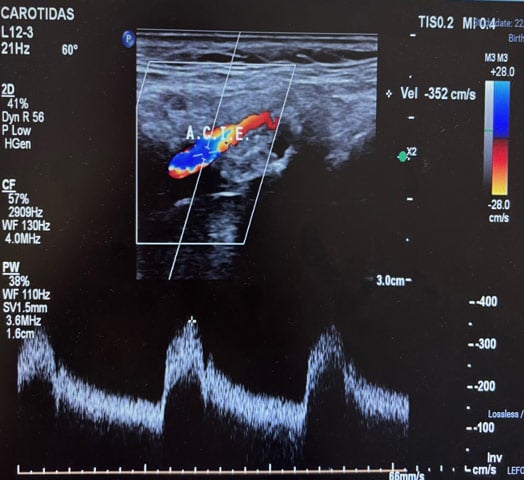
Carotid treatment
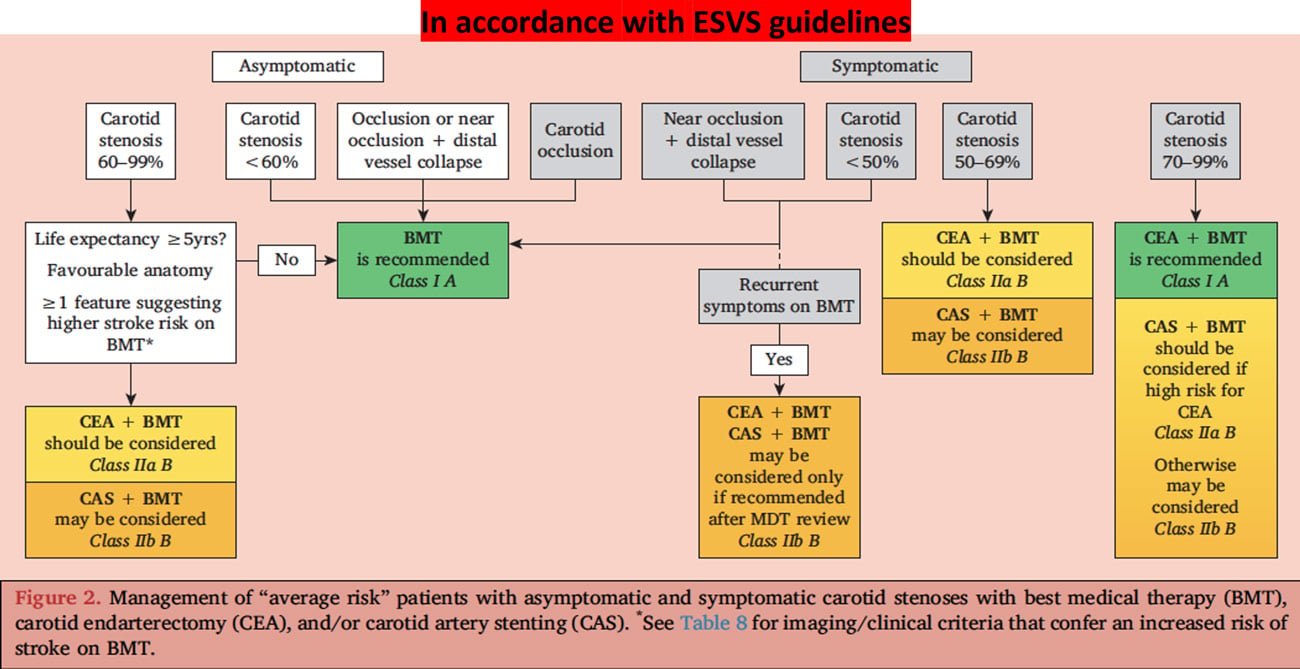
According to the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Atherosclerotic Carotid and Vertebral Artery Disease1, the management of carotid stenosis ranging from 60 % to 99 % is as follows:
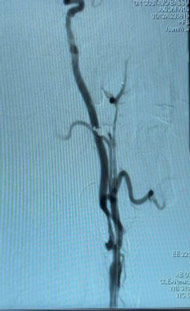
Procedure
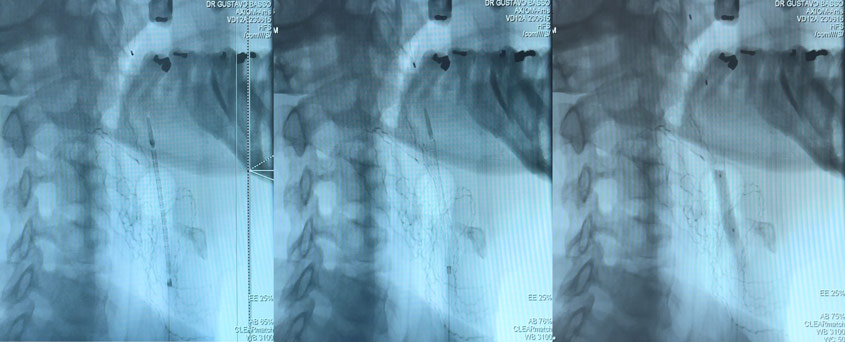
- Right CFA puncture, 5F short sheath
- Terumo 0,035 GW, Pigtail for arch angiogram / HH 5F Catheter to cannulate
- Left CEA catheterisation, exchange GW for Amplatz floppy short tip 1 cm
- Exchange catheter for long sheath 6F x 90 cm, positioned in left CCA (5.000UI IV heparin)
- Filter protection preparation (Captur 6 mm = Spider),
- Advance 0,014 GW through the ICA stenosis,
- Deployed at a straight position above the lesion
- PRE-Dilatation required? ➡️ Unnecessary for this case
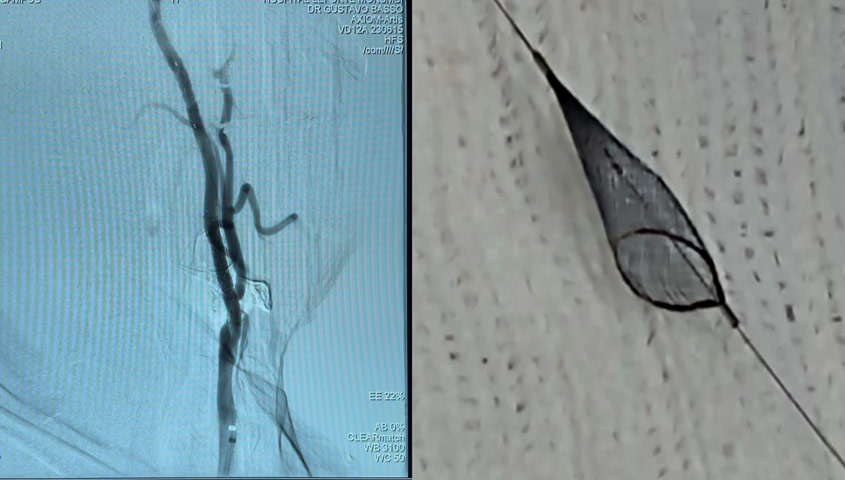
- MicroMesh stent C-GUARD 7 x 40 mm delivered on roadmapping
- Post dilatation 6 x 20mm for stent deployment completude
⚠️ Atropine ready for injection in case of significant bradycardia
Day+1 discharge
Reference:
- European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Atherosclerotic Carotid and Vertebral Artery Disease - Ross Naylor, Barbara Rantner, Stefano Ancetti, Gert J. de Borst, Marco De Carlo, Alison Halliday, Stavros K. Kakkos, Hugh S. Markus, Dominick J.H. McCabe, Henrik Sillesen, Jos C. van den Berg, Melina Vega de Ceniga, Maarit A. Venermo, Frank E.G. Vermassen - Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2023 - DOI: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2022.04.011
Get the latest clinical cases and breaking news delivered straight to your inbox!

