Total endo‑aortic repair for a triple‑lumen post‑dissection TAAA
A previously dissected thoraco‑abdominal aorta has morphed into an aneurysm fed by two competing false lumens—each nurturing vital visceral branches—while a compressed true lumen precariously threads between them.
- Objective: to protect all four visceral organs without open conversion.
- Key words: triple‑lumen, physician‑modified fenestration, multi‑access strategy, staged hybrid repair.
Can an endovascular plan out‑smart such anatomic chaos?
Core topics
- Chronic type‑A dissection & aneurysmal degeneration
- Triple‑lumen morphology
- Physician‑modified endografts
- Multi‑access cannulation techniques
- Staged versus one‑shot repair strategies
- Visceral‑ischaemia risk mitigation (SCI, renal, mesenteric)
Clinical presentation
- 63‑year‑old man with progressive back discomfort and enlarging thoraco‑abdominal aneurysm.
- Past interventions: 2 × TEVAR, 1 × open ascending repair, coil embolisation.
- Symptoms: mild post‑prandial abdominal pain; creatinine 92 µmol/L; no spinal‑cord deficit.
Risk assessment
- Anatomical: visceral supply entirely from FLs; prior grafts in thoracic aorta; compressed TL ≤ 6 mm; diameter 62 mm.
- Physiological: Creatinine 92 µmol/L; prior thoracic incision increases open‑redo risk.
- Neurological: extensive aortic coverage already → additive spinal‑cord ischaemia risk if full exclusion is attempted.
- Operative history: adhesions around prior thoracic graft; hostile abdomen for visceral debranching.
Current treatment options
- Redo open thoraco‑laparotomy with visceral re‑implantation.
- Hybrid debranching (visceral bypass + distal stent‑graft).
- Custom manufacturer‑built branched / fenestrated endograft (lead time ≥ 6 weeks).
- Physician‑modified endograft tailored on‑table.
- Conservative surveillance (risk of rupture > 15 % / yr).
Due to the complexity of the luminal architecture, conventional anatomical reconstruction was not feasible.
A physician-modified endograft (PMEG) was then used.
Overview of the customised endovascular strategy
Device: 200 mm thoracic stent‑graft (proximal Ø 30 mm → distal Ø 22 mm)
Fenestrations:
- 2 × 6 mm at 60 mm — targeting both renal arteries
- 2 × 8 mm at 95 mm — targeting the celiac trunk and SMA
Access Routes:
- Right common femoral artery — primary delivery through the true lumen
- Left common femoral artery — access to False Lumen 2 (celiac trunk + SMA)
- Left brachial artery — access to False Lumen 1 (bilateral renal arteries)
Staged approach: hybrid, sequentially securing each vascular territory to minimise the composite risk of major complications from a single extensive procedure
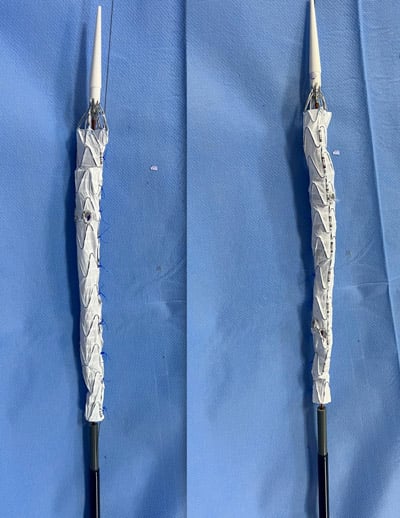
Operation steps
Bilateral femoral access was established, and the true lumen was carefully searched to obtain proper access. This approach ensured that the initial aorta could be reached from a more favorable route, taking advantage of the existing luminal architecture.
Using snare and the “through and through” technique, the true lumen of both iliac arteries was located, and guidewires and long sheath were advanced.
The PMEG was advanced to the proper position and released slowly until the RA fenestration opened. The L-RA was cannulated using a 150 cm slice guidewire, a 4F MPA catheter, and an 8F 90 cm sheath.
Due to the complex FL 1, a 5F VER catheter and snare from the left iliac artery re-entry tear were used to catch the R-RA guidewire and position it for cannulation in the FL 1.
An 8 mm balloon was used to expand narrowed true lumens outside the stent-graft.
The space surrounded by the intimal flap and expanded after dilation facilitated easy cannulation of the CT and SMA with a 6F steerable catheter.
The final angiography shows that all four vertebral vessels, the aortic stent graft, and the distal segment of the abdominal aorta are patent.
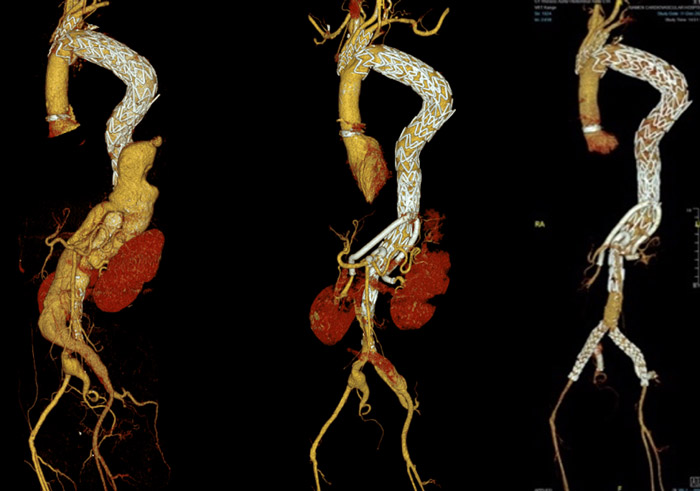
After one month, both iliac bifurcations were reconstructed with two fenestrated iliac extensions.
Six months later, the CTA showed the results of the total aortic repair.
Get the latest clinical cases and breaking news delivered straight to your inbox!

