Peripheral
Femoral bifurcation
How to manage CFA lesions with an endovascular approach?
Find out about the medical history of this 79-year-old man and tell us which option you would choose to treat him.
Part I - Medical History
History
- 2017 CABG
- 2018 CAS
- Moderate to severe COPD
Risk factors
- Obesity (BMI 31)
- Hypercholesterolemia
- NIDDM type 2
Present state
- Claudication 75 m left leg : Rutherford 3
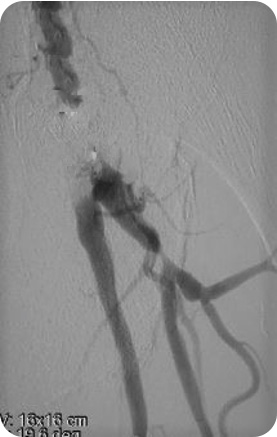
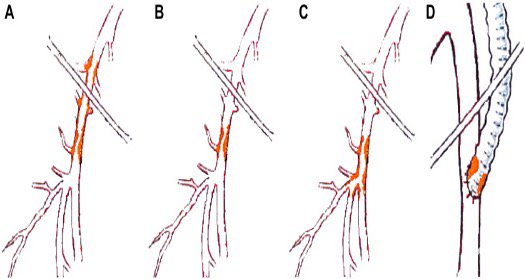
Azéma L. et al. EJVEVS, 41, 6 : June 2011 ; 787-793
Part II – Treatment & Conclusion
Getting access & passage
- Contralateral, cross-over approach
- RIM catheter, Glidewire 0,035”, Destination 6F,45cm
- Intraluminal passing
- 0,018” Advantage guidewire
- Fast spinning/drilling
Video 1
Video 2
Vessel preparation
- Low profile, high pressure balloons
- Scoring – cutting – sculpting
- (debulking)
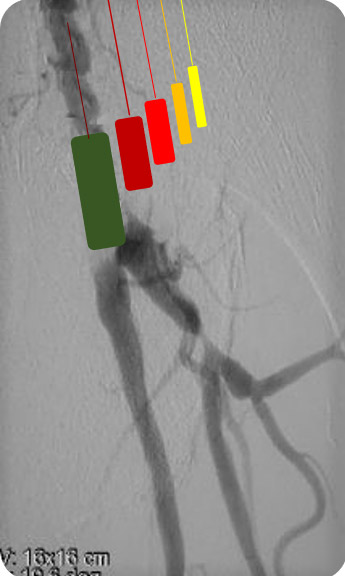
8-40 mm balloon
Vessel treatment
- Implantation SUPERA stent 7.5-40mm
- Meticulous nominal implantation
Video 3
Treatment deep femoral artery – final result
Advantage 0,018”-300cm
Armada 18 5-40mm
Video 6
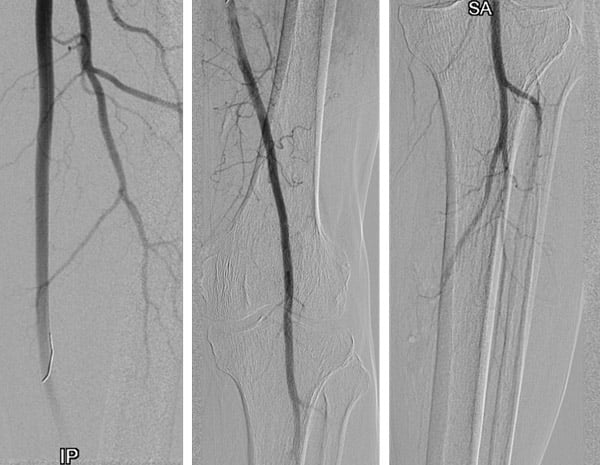
Answer
- Supera-stenting is a safe and effective endovascular alternative for surgery for a majority of CFA lesions treatment
- Vessel prep up to a 1(,1):1 RVD is mandatory ; if impossible, contra-indication for this technique
- Definitive treatment : Meticulous sizing & nominal implantation of SUPERA in perfect imaging circumstances
- The VMI-CFA trial showed good safety and efficacy results @24months with this technique.
- The SUPERSURGE RCT will offer more scientific insights in this topic -> an update will be expected during the upcoming PVI2023
Get the latest clinical cases and breaking news delivered straight to your inbox!

