Cases and resources in vascular techniques
This section provides a selection of cases and resources provided by experts in vascular techniques.
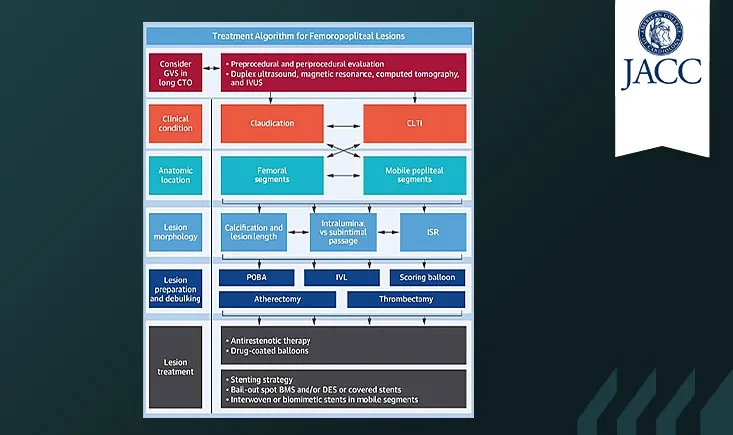
This article proposes a consensus-based algorithm for endovascular treatment of chronic femoropopliteal lesions, detailing imaging, lesion preparation, and definitive therapies to guide personalised treatment.
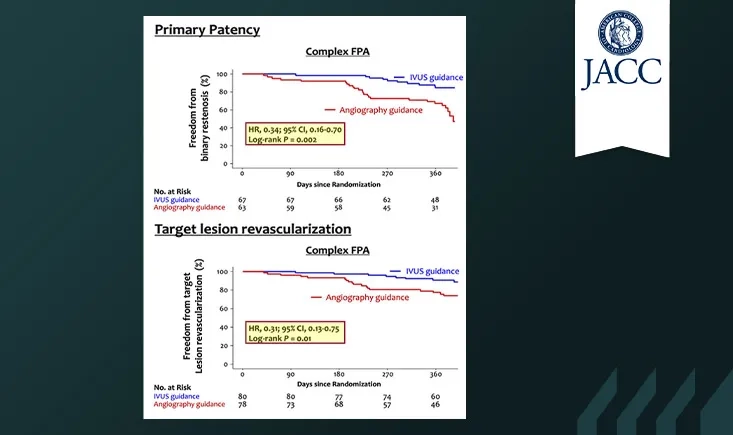
This subgroup analysis of the IVUS-DCB randomised trial compared IVUS- versus angiography-guided DCB angioplasty in patients with femoropopliteal artery disease. The results? IVUS significantly improved 12-month outcomes — but only in complex lesions. Get the details and clinical implications in this focused publication review.
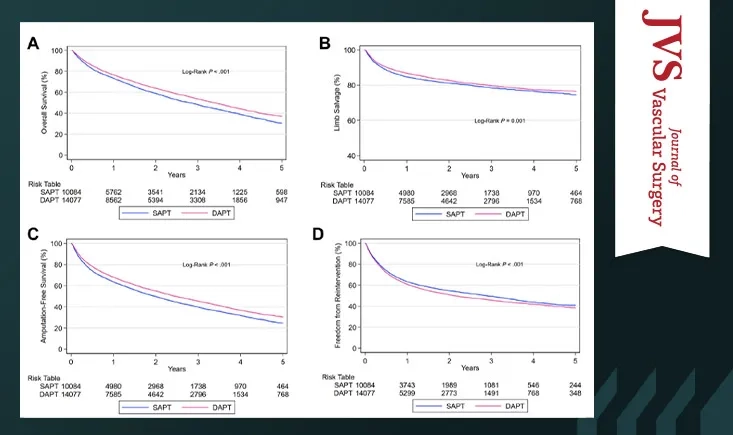
For patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI), the optimal antiplatelet strategy after infrainguinal endovascular intervention remains uncertain. This study uses data from the Vascular Quality Initiative–Medicare-linked database (2011–2019) to compare the impact of dual vs. single antiplatelet therapy on amputation-free survival at 1 and 5 years.
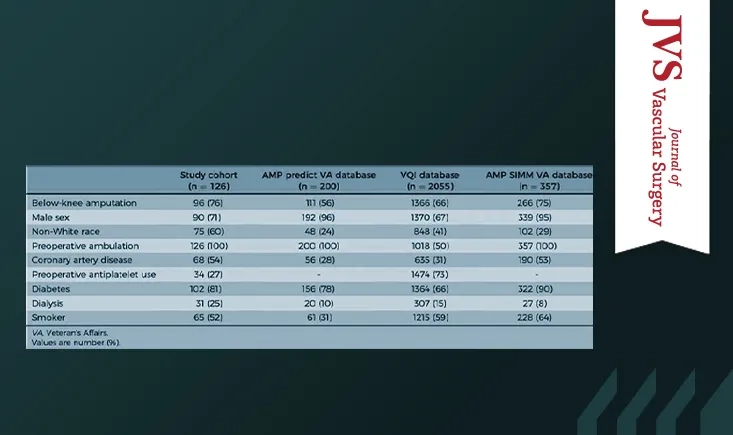
This retrospective study evaluated the accuracy of three predictive models for post-amputation mobility in a real-world, disadvantaged population. Results showed significant discrepancies between predicted and actual outcomes, questioning the reliability of these tools outside their original development settings.
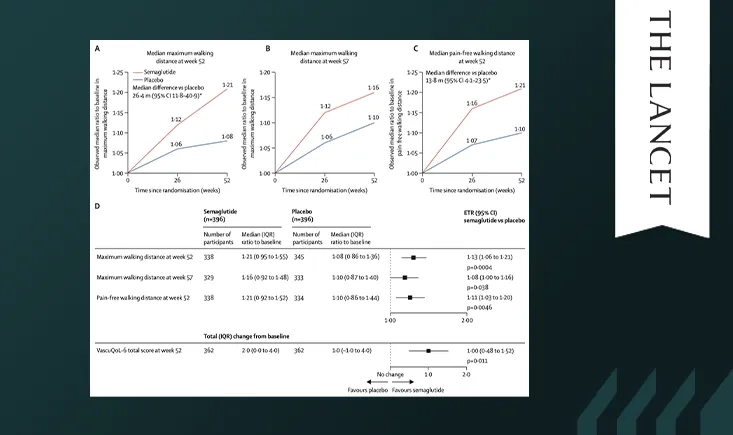
In patients with PAD and type 2 diabetes, semaglutide significantly improved walking distance, symptoms, and quality of life over 52 weeks, supporting its use in this high-risk population.
Sex-based differences in peripheral arterial disease (PAD) are real — and often overlooked. This AHA scientific statement highlights key disparities in epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes, and outlines priorities to improve care for all patients.
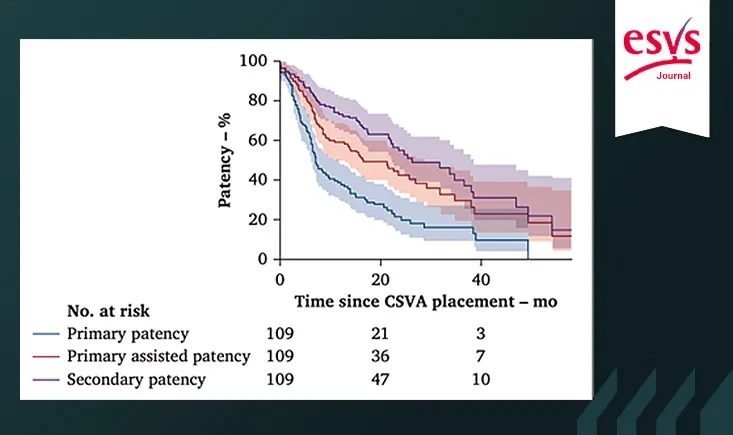
This retrospective two-center study evaluated the outcomes of cold-stored saphenous vein allografts (CSVAs) for hemodialysis access in 109 patients with end-stage renal disease. The results showed primary patency rates comparable to those of ePTFE grafts, with a lower risk of infection—supporting CSVAs as a promising alternative for vascular access in selected patients.
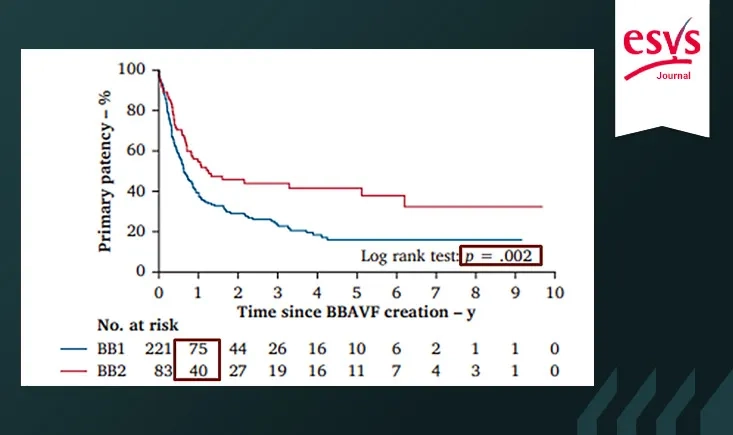
This large nationwide Swedish registry study compared the outcomes of both techniques in adult patients requiring a brachiobasilic arteriovenous fistula. While the two-stage procedure offered better primary patency, it also delayed functional use. Long-term results were similar, underscoring the need for individualized surgical decisions.
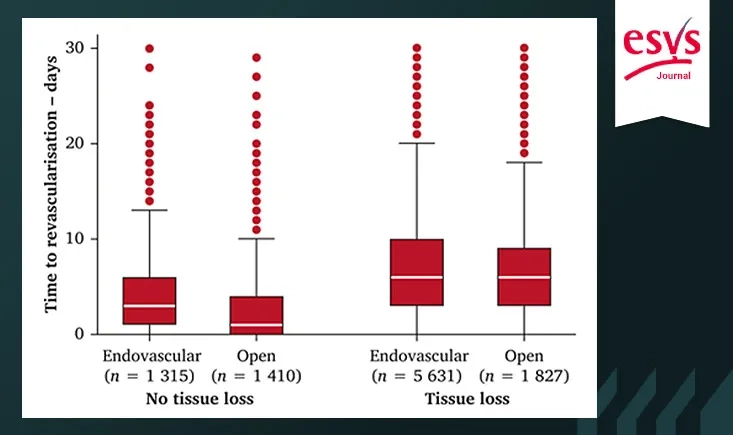
This study examines the effect of revascularisation timing on mortality and amputation rates in emergency CLTI patients. It found that delays, especially in those with tissue loss, led to higher one-year mortality, emphasizing the need for prompt treatment.
This single-center retrospective study assessed the safety and efficacy of popliteal access for endovascular treatment of iliofemoral occlusive disease in an office-based setting. Findings suggest that popliteal access is a safe and effective alternative for complex iliofemoral disease in outpatient care.